- Home
- Faq
- Technical Support
- How do you read the insulation level on the motor nameplate?
How do you read the insulation level on the motor nameplate?
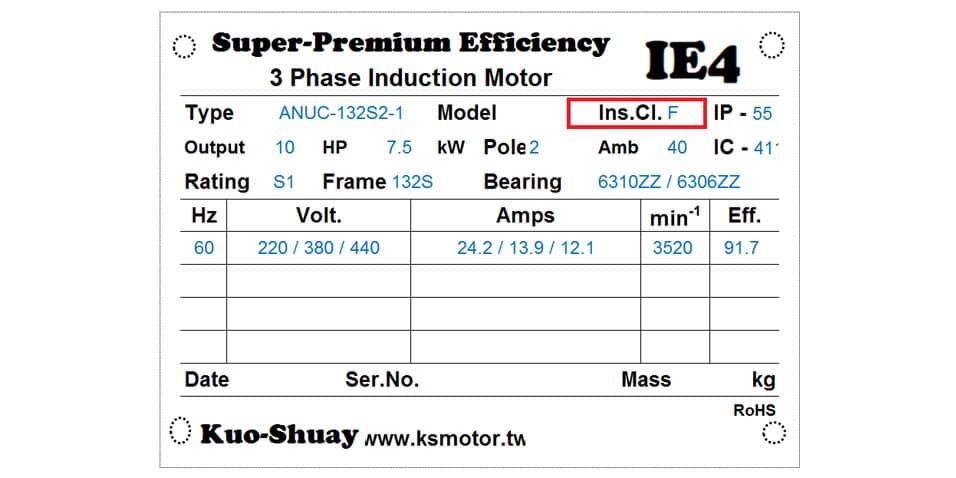
How to distinguish the insulation level of motors
When you look at the motor nameplate, you can see the insulation level marked with English letters, and this level refers to the heat resistance level of the insulation material selected for the motor, because the insulation ability is related to the heat resistance level. High temperatures The ability of the insulating material will deteriorate when the motor is running, so it is necessary to select the appropriate insulation level and material according to the temperature at which the motor is running. There are five common insulation grades, namely A, E, B, F, and H. Each grade represents a different degree of temperature resistance. If it is used beyond its maximum temperature resistance, the motor is likely to burn out or have a reduced lifespan.
Generally speaking, ICE motor use insulation class E(120°C), B(130°C) and F(155°C). Although the IE3 motors have lower temperature rise, we still choose F class insulation. It makes the motor more durable when operated with high temperature. For special application, such as oven or electric carrier motor, we will choose H class insulation, which help the motor withstand the higher temperature.
Insulation classes for electric equipment
In 1977, the Electric Instrument Rules Committee of the Japanese Industrial Standards Committee discussed the classes of electrical insulation and drew up JIS C 4003: Classes of electrical insulation, to clarify the classes of motor insulation and their maximum allowable temperatures.
Insulation Classification
Class Y: Withstands a temperature of up to 90°C; typically made of cotton, silk, or paper
Class A: Withstands a temperature of up to 105°C; reinforced Class-Y materials with impregnated varnish or insulation oil
Class E : Withstands a temperature of up to 120°C
Class B : Withstands a temperature of up to 130°C. This has a form that inorganic material is hardened with adhesives. This is the first insulator using this structure.
Class F : Withstands a temperature of up to 155°C; for example, made of Class-B materials that are upgraded with adhesives, silicone, and alkyd-resin varnish of higher thermal endurance
Class H : Withstands a temperature of up to 180°C; for example, made of inorganic material glued with silicone resin or adhesives of equivalent performance
Class C : insulation: Withstands a temperature of up to 180°C or higher; made of 100% inorganic material As explained above, electrical insulation is classified with its maximum allowable temperature. By adopting an insulation technique of higher thermal endurance, electric instruments can be downsized.
Importance of insulation level
The insulation level is a classification made to ensure the safety and reliability of motor operation. It is one of the important indications on the motor nameplate and has the following important purposes:
Safety
The insulation level ensures that the motor is protected against the risk of electric shock and fire in the event of an electrical fault. If the insulation is insufficient to withstand a specific voltage, insulation damage can occur, resulting in electrical failure and danger.
Reliability
Motors with high insulation levels are often able to run longer without the need for repair or replacement. This helps reduce operating costs, reduce downtime and increase productivity.
Adaptability
Different application scenarios require motors with different insulation levels. Typically, high temperature or high humidity environments require higher insulation levels for motors to ensure they can operate properly without being damaged by environmental factors.
Comply with regulations
Regulations and standards on electrical equipment in many countries and regions require the use of motors with specific insulation levels. These regulations are designed to ensure public safety and protect the environment.
Therefore, it is very important to distinguish and mark the insulation level of the motor to ensure the safe operation of the motor, extend its life, improve efficiency, and comply with relevant regulatory requirements. Selection of the appropriate insulation level depends on the needs of the specific application and the characteristics of the operating environment.
